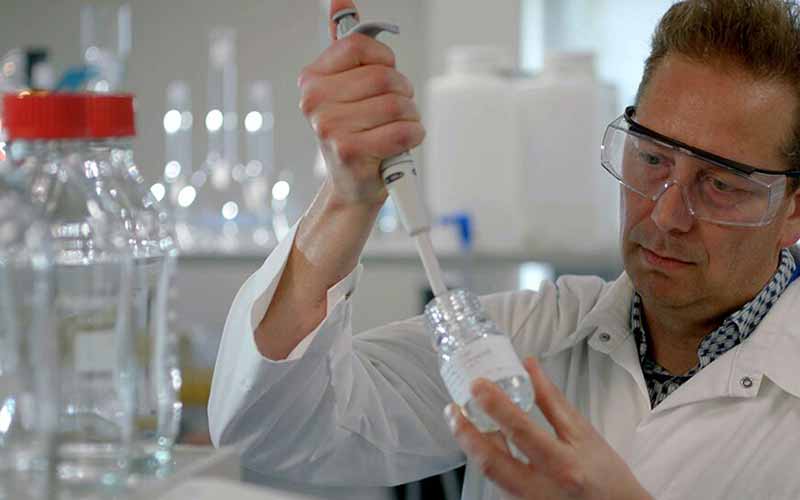
A particular challenge in medical applications is the need to keep products sterile – free from harmful contaminants such as fungi, bacteria, viruses and spores. The following introduces several main sterilization methods and their principles.
1.Physical Sterilization
Autoclave Sterilization is one of the main method of phisical sterilization.
Principles of Autoclave Sterilization:
An autoclave is a vessel similar to a pressure cooker. The object to be sterilized is placed in it and then sealed. Next, high temperature steam is charged under high pressure to replace air. Moist heat kills microorganisms by irreversible coagulation and denaturation of enzymes and structural proteins. The time and temperature for this to happen depends on the pressure and the type of microorganisms being killed. After the necessary time has elapsed, the steam is released and the sterilized object is removed. The entire cycle lasts 15 to 60 minutes (batch processing).
2.Chemicall Sterilization
There are many chemical methods that can be used for sterilization in the medical field. The following example is EO sterilization.
Principles of Ethylene oxide (ETO) sterilization:
An ETO sterilizer is a container that holds objects to be sterilized. The basic ETO sterilization cycle consists of 5 steps (steam evacuation, gas injection, diffusion, evacuation, and air flush) and takes approximately 2 1/2 hours, excluding ventilation time (to drain the ETO). Mechanical ventilation requires 8 to 12 hours at +50 to +60°C; passive ventilation is also possible, but may take 7 days. After the ventilation is completed, the sterilized object (batch) is removed. ETO chemically reacts with amino acids, proteins and DNA to prevent microbial reproduction.
3.Radiation Sterilization
Gamma Sterilization and Electron Beam Sterilizationare the teo main methods.
(1) Principles of Gamma Sterilization:
The object to be sterilized is placed on a conveyor, which is brought near a source of strong gamma radiation, such as cobalt-60. After the object to be sterilized stops in the radiation field, it receives a certain dose, and then moves the conveyor to continue processing the next object. Instead of stop-and-go, the conveyor may also move continuously (continuous processing) at a certain speed (to ensure proper dose). Ionizing radiation produces excitation, ionization, and in the presence of water, the formation of free radical structures. Free radicals are strong oxidizing (OH, HO2) and reducing (H) agents capable of destroying essential molecules in living cells. Therefore, all three processes result in the fission of essential cellular components, such as enzymes and DNA. resulting in cell death. The most severe form of biological damage to gamma radiation occurs within the gamma-ray window, between 3 MeV and 10 MeV. Cobalt 60 emits gamma radiation at 1.17MeV and 1.33MeV levels, slightly below the most effective range.
(2)Principles of Electron Beam Sterilizationare:
The object to be sterilized is placed on the conveyor and slowly passed through the window of the electron beam generator. The speed of the conveyor is chosen to ensure the proper radiation dose (continuous treatment). Achieving the penetration depth required for sterilization requires energy levels on the order of 5MeV to 10MeV. Electron beam radiation forms free radicals that react with macromolecules, thereby damaging DNA and causing cell death. The method is capable of destroying all types of pathogens, including viruses, fungi, bacteria, worms, spores, and molds.
Ruilabels is a professional label supplier in China. We offer labels stickers for Sterilization Applications Solutions . Welcome to contact us buy the high quality label with competitive price.